Présentation
Thymic epithelial tumors (TETs) are rare and potentially agressive intrathoracic malignant cancers difficult to treat. They include thymomas and thymic carcinomas. Reported incidence is estimated between 1.3 and 1.7 per million per year. Annual incidence ranging from <1 (North-Est Europe) and 2 to 3.5/million inhabitants in Central-South continent. Mean age at diagnosis is 40 to 50 years. Approximately 30% of patients also have Myasthenia Gravis. Thymic gland has a lymphocyte and an epithelial component. Only the epithelial component could develop tumour. We can differentiate between encapsulated tumours (stage I in the Masaoka classification, 65% of cases), or invasive tumours (stages II-IV in the Masaoka classification, 35% of cases). Many histological classifications have been proposed. At International Thyme Malignancy Interest Group (ITMIG) consensus meeting in 2011, the World Health Organization (WHO) was validated as the standard for clinical practice. A wide variety of histological subtypes are included in TETs, associated with different clinical outcomes. Thymomas (T) are subdivided into different subtypes (A, AB, B1, B2, B3) based upon the morphology of epithelial tumour cells and lymphocytic component (WHO Classification 2004-2014). Thymic carcinomas (CT) are frequently associated with poor prognosis and the development of distant metastases. IASLC together with ITMIG proposed a consensus TNM based-staging system in 2011 according with Masaoka-Koga classification. Surgery represents the first step of the treatment, as it is the case in Masaoka-Koga stage I/II and some stage III tumours (classified as stage I, II, IIIA/T3 in the IASLC/ITMIG TNM proposed classification). However, approximately one third of these patients will present a recurrence. There is no strong evidence of postoperative treatment. Platinum-based chemotherapy is standard treatment for metastasic, unresectable and/or recurrent disease. Combination regimens with anthracyclines response rate vary from 69% in T to 42% in CT. In addition to multiagent chemotherapy combinations, the efficacy of other types of therapies such as sunitinib and everolimus has been demonstrated. Immunotherapy has shown promising results but its use is limited due to the frequence occurence of auto-immune disease that are a contraindication. Nevertheless, the estimated five years overall survival (OS) for T is 80%, and 40% for patients with CT. TETs mutational profile is poorly detectable by gene panels used for molecular profiling of common solid tumors, KIT mutations being the only potential target identified in up to 10% of the tumors. Additionally, no large study has correlated the a complete molecular profile with tumor subtype or the occruence of an auto-immune disease.
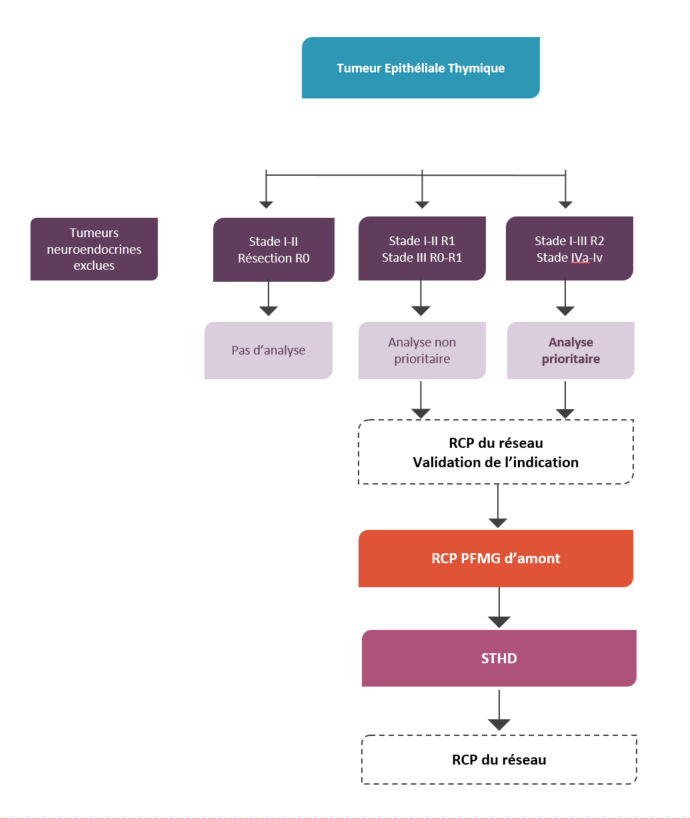
Critères avant d'envisager une discussion en RCP
- PS 0 à 2
- Eligible à un traitement systémique
- Préciser le type d’auto-immunité
- Préciser les antécédents de cancers et d’irradiation de la zone biopsiée
- Disponibilité : tissus sain et tumoral congelés
Place du STHD dans la stratégie de prise en charge
RCP Tumeurs épithéliales thymiques
Benjamin Besse
Benjaminbesse@gustaveroussy.fr
Nicolas Girard
Nicolas.girard2@curie.fr
RCP FMG Tumeurs solides Adultes AP-HP Paris
Camille TLEMSANI
RCP FMG Tumeurs solides Adultes Curie Paris
Maud KAMAL
RCP FMG Tumeurs solides Adultes Gustave Roussy Villejuif
Claudio NICOTRA
RCP FMG Tumeurs solides Adultes Rennes
Thierry Lesimple
Julien Edeline
Thibault De La Motte Rouge
Thierry Fest
Alexandra Lespagnol
RCP FMG Tumeurs solides Adultes Brest
RCP FMG Tumeurs solides Adultes Angers
RCP FMG Tumeurs solides Adultes Nantes
RCP FMG Tumeurs solides Adultes Tours
M. ROMOLI Arnaud
RCP FMG Tumeurs solides Adultes Caen
Elodie Coquan
George Emile
Florence Joly-Lobbedez
RCP FMG Tumeurs solides Adultes Amiens
Bruno CHAUFFERT
Claire POULET
Julie DREMAUX
RCP FMG Tumeurs solides Adultes Lille
RCP FMG Tumeurs solides Adultes Strasbourg
Philippe BARTHELEMY
RCP FMG Tumeurs solides Adultes Dijon
François GHIRINGHELLI
RCP FMG Tumeurs solides Adultes CLB Lyon
Olivier TREDAN
RCP FMG Tumeurs solides Adultes CITOHL Lyon
Benoît YOU
RCP FMG Tumeurs solides Adultes APHM Marseille
Pascale TOMASINI
RCP FMG Tumeurs solides Adultes IPC Marseille
François BERTUCCI
RCP FMG Tumeurs solides Adultes Montpellier
Stanislas Quesada
RCP FMG Tumeurs solides Adultes Nice
Esma SAADA-BOUZID
RCP FMG Tumeurs solides Adultes Toulouse
Carlos GOMEZ-ROCA
RCP FMG Tumeurs solides Adultes Bergonié Bordeaux
Antoine ITALIANO
RCP FMG Tumeurs solides Adultes CHU Bordeaux
Pr MERLIO Jean-Philippe